Have you ever been captivated by the enchanting scent of a well-crafted perfume, where the moment you spritz it on, you may feel transformed, more confident, or even uplifted? Have you ever wondered what goes into creating those delightful fragrances that impact our lives?
Let us explore the intricate process of perfume creation, the science behind it, and the innovative technology that makes it all possible!
A Brief History of Perfume
For a deeper dive into the history of perfume, be sure to read this detailed article that explores its fascination evolution.
The Building Blocks of Fragrance: Ingredients
1. Essential Oils
At the heart of any perfume are essential oils, which are concentrated plant extracts. These oils capture the essence of flowers, fruits, spices, and other botanicals. For instance:
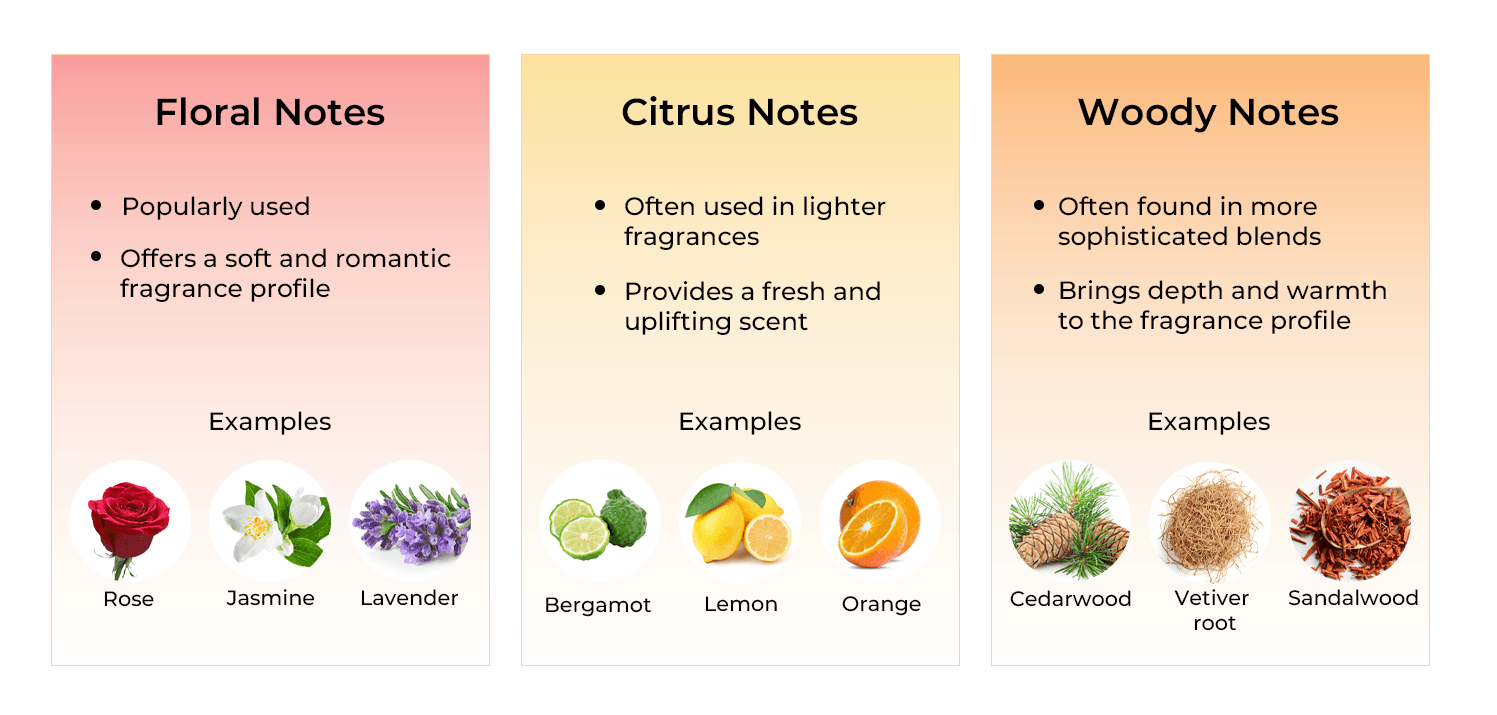
2. Aroma Compounds
In addition to natural oils, perfumers utilize synthetic aroma compounds, which mimic natural scents or create new fragrances that cannot be found in nature. For example, vanillin, which mimics the scent of vanilla, is a popular synthetic addition to many sweet and gourmand fragrances.
3. Fixatives
To ensure the longevity of scents, perfumers use fixatives, which are substances that help stabilize and prolong fragrance. Traditional fixatives include resins such as myrrh and labdanum, as well as animal-derived ingredients such as ambergris.
4.Solvents and Alcohols
Finally, the mixture of essential oils and aroma compounds is dissolved in alcohol or another solvent. Ethanol is commonly used, as it evaporates quickly and carries the fragrance effectively. It’s important for perfumers to select the right concentration of alcohol in order to enhance the fragrance’s projection and longevity.
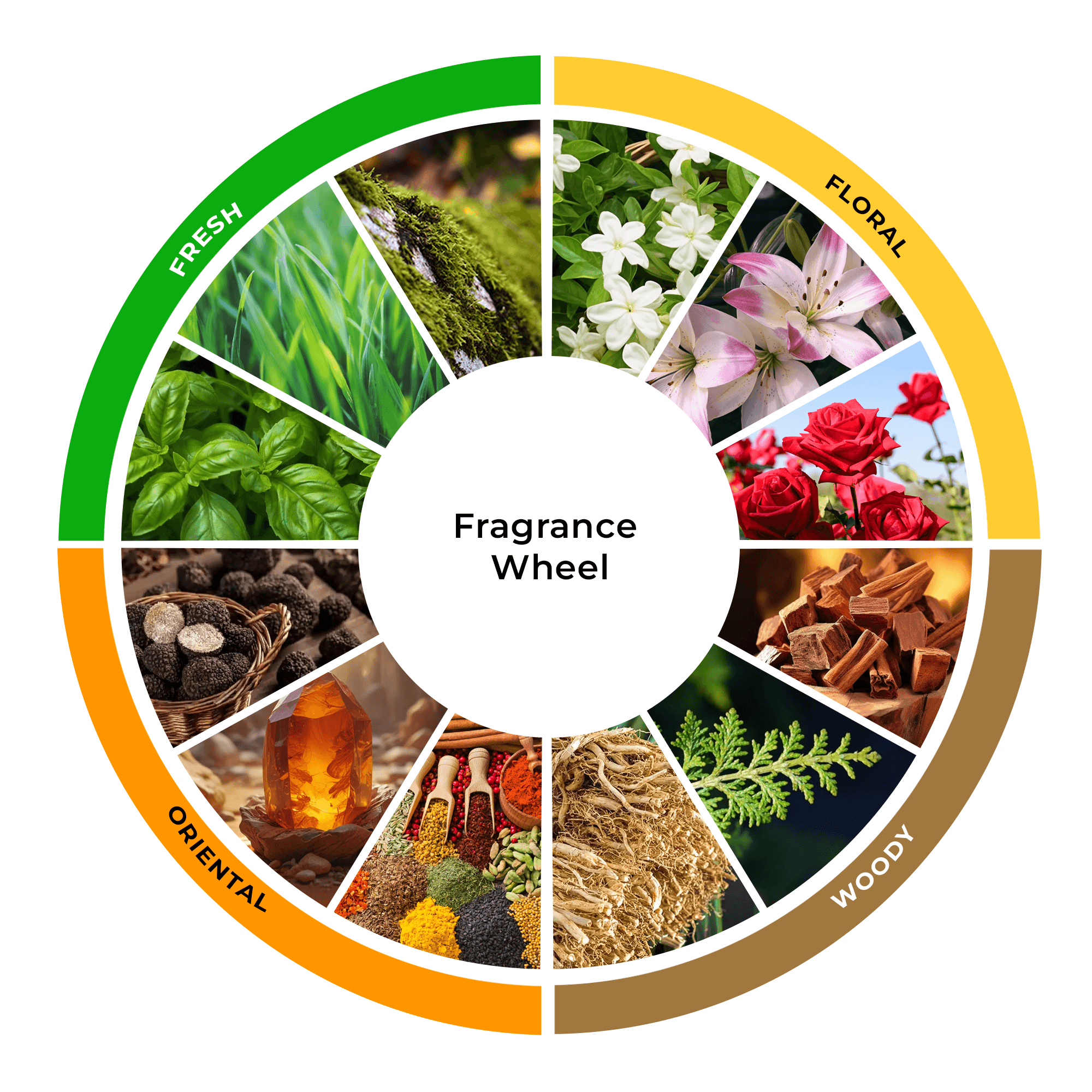
Floral: Dominated by flower scents; tender and romantic.
Woody: Earthy and grounding, with notes like sandalwood and vetiver.
Oriental: Rich and warm, featuring spices and vanilla; often quite sensual.
Fresh: Bright and clean, typically containing citrus and green notes.
Furthermore, each perfume will have top, middle, and base notes. For more information on these notes, click here.
Chapter 4: The birth of contemporary perfumery
1. Scent Extraction Techniques
There are various techniques that Modern perfumery employs to extract essential oils:
Steam Distillation: A method which is commonly used to obtain essential oils from plants, where steam passes through the plant materials and carries the volatile compounds.
Solvent Extraction: Used for delicate flowers, where solvents dissolve fragrant compounds without heat damage.
Cold Pressing: Often used for citrus oils, it involves mechanically pressing peels to extract the oils.
2. The Use of AI and Data Analytics
With the evolution of technology, perfumers are currently utilizing AI and data analytics to predict trends and create innovative fragrances. By analyzing customer preferences and market demands, AI-driven tools can propose unique combinations of notes to create mesmerizing scents.
3.Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
In order to enhance the shopping experience of customers, some avant-garde perfume houses use virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Customers can virtually “smell” fragrances, visualize the scent ingredients in an immersive environment, and select fragrances based on their mood or personal style.
When Chanel No. 5 hit the market in 1921, it revolutionised everything! Its harmonious blend of sandalwood, rose, jasmine, and more, set the stage for modern perfumes that mix luxury with science and art.
The Creation Process: From Concept to Bottle
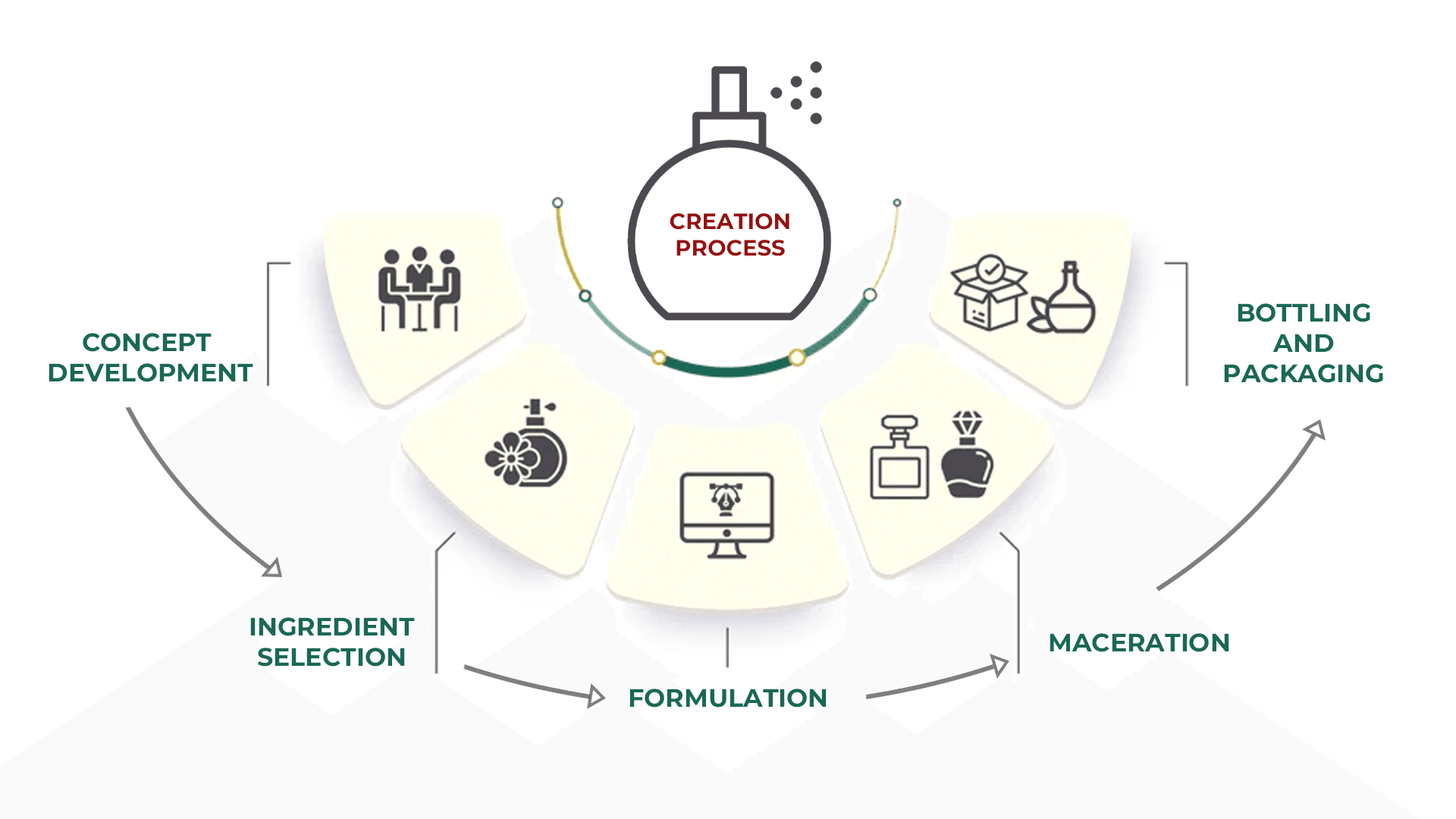
Every perfume creation starts with a vision. Perfumers often draw inspiration from emotions, experiences, or even art, and they jot down notes, draw sketches, or create mood boards to capture their ideas.
Step 2: Ingredient Selection
Once the concept is established, perfumers select essential oils, aroma compounds, and fixatives that align with their vision. This selection process involves a deep understanding of scent interactions and personal preferences.
Step 3: Formulation
Using their knowledge and expertise, perfumers create hundreds of test formulations, making minute adjustments until they reach the desired scent profile. This iterative process can often take months of experimentation.
Step 4: Maceration
Once a final formulation is established, the mixture undergoes maceration—a period where it rests to allow the ingredients to meld and mature, thus enhancing the depth of the fragrance.
Step 5: Bottling and Packaging
After maturation, the perfume is filtered and bottled, making it ready for distribution. The packaging is crucial to branding as it reflects the identity and marketing strategy of the fragrance.
Whether you’re a fragrance enthusiast or simply curious about scent-making, we hope this behind-the-scenes look at perfumery has deepened your appreciation for this enchanting world. After all, every scent tells a story—what will yours be?

